Fulton County, Pennsylvania
Fulton County | |
|---|---|
 The Fulton County Courthouse | |
 Location within the U.S. state of Pennsylvania | |
 Pennsylvania's location within the U.S. | |
| Coordinates: 39°55′N 78°07′W / 39.92°N 78.11°W | |
| Country | |
| State | |
| Founded | April 19, 1850 |
| Named for | Robert Fulton |
| Seat | McConnellsburg |
| Largest borough | McConnellsburg |
| Area | |
• Total | 438 sq mi (1,130 km2) |
| • Land | 438 sq mi (1,130 km2) |
| • Water | 0.5 sq mi (1 km2) 0.1% |
| Population (2020) | |
• Total | 14,556 |
| • Density | 33/sq mi (13/km2) |
| Time zone | UTC−5 (Eastern) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−4 (EDT) |
| Congressional district | 13th |
| Website | www |
Fulton County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, the population was 14,556,[1] making it the fourth-least populous county in Pennsylvania. Its county seat is McConnellsburg.[2] The county was created on April 19, 1850,[3] from a part of Bedford County and named after inventor Robert Fulton.[4] The county is part of the Southwest Pennsylvania region of the state.[a]
Geography
[edit]According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of 438 square miles (1,130 km2), of which 438 square miles (1,130 km2) is land and 0.5 square miles (1.3 km2) (0.1%) is water.[5] It is in the watershed of the Chesapeake Bay and, although most of the county is drained by the Potomac River, some northern and northeastern areas are drained by the Juniata River into the Susquehanna River. It has a humid continental climate (Dfa/Dfb) and average monthly temperatures in McConnellsburg range from 29.2 °F in January to 73.0 °F in July.[6] Fulton County is one of the 423 counties served by the Appalachian Regional Commission,[7] and it is identified as part of "Greater Appalachia" by Colin Woodard in his book American Nations: A History of the Eleven Rival Regional Cultures of North America.[8]
Adjacent counties
[edit]- Huntingdon County (north)
- Franklin County (east)
- Washington County, Maryland (south)
- Allegany County, Maryland (southwest)
- Bedford County (west)
Geology
[edit]Fulton County is situated within the Ridge and Valley physiographic province, which is characterized by folded and faulted sedimentary rocks of early to middle Paleozoic age.[9]
The stratigraphic record of sedimentary rocks within the county spans from the Cambrian Shadygrove Formation outcropping just south of McConnellsburg to the Pennsylvanian Allegheny Group at the northernmost tip of the county. No igneous or metamorphic rocks of any kind exist within Fulton county.
Mountain ridges within Fulton County include Rays Hill (along the western border with Bedford County), Town Hill, Sideling Hill, Scrub Ridge, and Meadow Grounds Mountain, and all these are held up by the Mississippian Pocono Formation, made of quartz sandstone and conglomerate. Rays Hill and Town Hill form a syncline, as do Scrub Ridge and Meadow Grounds Mountain, and Sideling Hill itself is a syncline. Dickeys Mountain and Tuscarora Mountain (along the eastern border with Franklin County) also form a syncline, but these ridges are held up by the Tuscarora Formation. Broad Top, located in the northeast corner of the county, is a plateau of relatively flat-lying rocks that are stratigraphically higher, and thus younger (Mississippian and Pennsylvanian), than most of the other rocks within the county. Broad Top extends into Huntingdon County to the north and Bedford County to the west.
All of Fulton County lies far to the south of the terminal moraine, and thus it was never glaciated.[10] However, during the Pleistocene epoch, or "Ice Age," periglacial (meaning "around glacier" or simply "cold") processes dominated. Most of the county was most likely a tundra during the Pleistocene.
The Broad Top Coal Field is located in Wells Township in the northwestern corner of the county.[11] The field contains bituminous coal. There are a few abandoned mines in the area, although acid mine drainage is not as much of an environmental problem in Fulton County as it is in adjacent Bedford and Huntingdon Counties.
Interesting geologic features within Fulton County include some of the following:
- The Meadow Grounds syncline west of McConnellsburg.
- A transpression structure is located on the east side of the Meadow Grounds syncline. This structure consists of a complex set of up-thrust fault blocks of Silurian and Devonian rocks bounded on all sides by north-trending faults.
Demographics
[edit]| Census | Pop. | Note | %± |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1850 | 7,567 | — | |
| 1860 | 9,131 | 20.7% | |
| 1870 | 9,360 | 2.5% | |
| 1880 | 10,149 | 8.4% | |
| 1890 | 10,137 | −0.1% | |
| 1900 | 9,924 | −2.1% | |
| 1910 | 9,703 | −2.2% | |
| 1920 | 9,617 | −0.9% | |
| 1930 | 9,231 | −4.0% | |
| 1940 | 10,673 | 15.6% | |
| 1950 | 10,387 | −2.7% | |
| 1960 | 10,597 | 2.0% | |
| 1970 | 10,776 | 1.7% | |
| 1980 | 12,842 | 19.2% | |
| 1990 | 13,837 | 7.7% | |
| 2000 | 14,261 | 3.1% | |
| 2010 | 14,845 | 4.1% | |
| 2020 | 14,556 | −1.9% | |
| [12] | |||
As of the census[13] of 2000, there were 14,261 people, 5,660 households, and 4,097 families residing in the county. The population density was 33 people per square mile (13 people/km2). There were 6,790 housing units at an average density of 16 units per square mile (6.2/km2). The racial makeup of the county was 98.25% White, 0.66% Black or African American, 0.20% Native American, 0.11% Asian, 0.01% Pacific Islander, 0.04% from other races, and 0.72% from two or more races. 0.36% of the population were Hispanic or Latino of any race. 40.8% were of German, 20.4% American, 8.3% Irish and 6.9% English ancestry.
There were 5,660 households, out of which 31.70% had children under the age of 18 living with them, 59.50% were married couples living together, 8.20% had a female householder with no husband present, and 27.60% were non-families. 24.00% of all households were made up of individuals, and 10.60% had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.50 and the average family size was 2.95.
In the county, the population was spread out, with 24.60% under the age of 18, 7.60% from 18 to 24, 28.40% from 25 to 44, 25.00% from 45 to 64, and 14.50% who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 38 years. For every 100 females there were 100.10 males. For every 100 females age 18 and over, there were 98.60 males.
Almost everyone who lives in Fulton County speaks English as their first language. The dominant form of speech in Fulton County is the Central Pennsylvania accent.
2020 census
[edit]| Race | Num. | Perc. |
|---|---|---|
| White (NH) | 13,726 | 94.3% |
| Black or African American (NH) | 124 | 0.85% |
| Native American (NH) | 25 | 0.17% |
| Asian (NH) | 41 | 0.3% |
| Pacific Islander (NH) | 3 | 0.02% |
| Other/Mixed (NH) | 491 | 3.4% |
| Hispanic or Latino | 146 | 1% |
Politics
[edit]| Year | Republican | Democratic | Third party(ies) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. | % | No. | % | No. | % | |
| 2024 | 7,039 | 86.03% | 1,102 | 13.47% | 41 | 0.50% |
| 2020 | 6,824 | 85.41% | 1,085 | 13.58% | 81 | 1.01% |
| 2016 | 5,694 | 83.47% | 912 | 13.37% | 216 | 3.17% |
| 2012 | 4,814 | 77.38% | 1,310 | 21.06% | 97 | 1.56% |
| 2008 | 4,642 | 73.61% | 1,576 | 24.99% | 88 | 1.40% |
| 2004 | 4,772 | 76.10% | 1,475 | 23.52% | 24 | 0.38% |
| 2000 | 3,753 | 71.01% | 1,425 | 26.96% | 107 | 2.02% |
| 1996 | 2,665 | 54.75% | 1,620 | 33.28% | 583 | 11.98% |
| 1992 | 2,558 | 50.93% | 1,588 | 31.61% | 877 | 17.46% |
| 1988 | 3,086 | 66.42% | 1,532 | 32.97% | 28 | 0.60% |
| 1984 | 3,254 | 71.14% | 1,309 | 28.62% | 11 | 0.24% |
| 1980 | 2,740 | 64.90% | 1,342 | 31.79% | 140 | 3.32% |
| 1976 | 2,219 | 54.76% | 1,737 | 42.87% | 96 | 2.37% |
| 1972 | 2,515 | 66.24% | 1,192 | 31.39% | 90 | 2.37% |
| 1968 | 2,200 | 55.37% | 1,174 | 29.55% | 599 | 15.08% |
| 1964 | 1,747 | 44.37% | 2,180 | 55.37% | 10 | 0.25% |
| 1960 | 2,698 | 61.61% | 1,672 | 38.18% | 9 | 0.21% |
| 1956 | 2,370 | 56.50% | 1,819 | 43.36% | 6 | 0.14% |
| 1952 | 2,127 | 55.12% | 1,718 | 44.52% | 14 | 0.36% |
| 1948 | 1,760 | 50.65% | 1,684 | 48.46% | 31 | 0.89% |
| 1944 | 2,084 | 54.03% | 1,758 | 45.58% | 15 | 0.39% |
| 1940 | 2,108 | 51.46% | 1,982 | 48.39% | 6 | 0.15% |
| 1936 | 2,085 | 46.02% | 2,431 | 53.65% | 15 | 0.33% |
| 1932 | 1,410 | 41.83% | 1,921 | 56.99% | 40 | 1.19% |
| 1928 | 2,179 | 66.82% | 1,054 | 32.32% | 28 | 0.86% |
| 1924 | 1,160 | 47.64% | 1,207 | 49.57% | 68 | 2.79% |
| 1920 | 1,292 | 50.19% | 1,231 | 47.82% | 51 | 1.98% |
| 1916 | 802 | 39.62% | 1,199 | 59.24% | 23 | 1.14% |
| 1912 | 317 | 15.34% | 1,080 | 52.25% | 670 | 32.41% |
| 1908 | 974 | 45.45% | 1,098 | 51.24% | 71 | 3.31% |
| 1904 | 1,100 | 48.48% | 1,137 | 50.11% | 32 | 1.41% |
| 1900 | 1,039 | 45.27% | 1,224 | 53.33% | 32 | 1.39% |
| 1896 | 1,083 | 45.83% | 1,246 | 52.73% | 34 | 1.44% |
| 1892 | 918 | 42.74% | 1,210 | 56.33% | 20 | 0.93% |
| 1888 | 951 | 42.93% | 1,230 | 55.53% | 34 | 1.53% |
Although Fulton County traditionally voted Democratic in the 19th and early 20th centuries, and Democrats held the edge in voter registration in the county until the late 20th century, it has displayed strong tendencies to vote for Republican candidates since the New Deal era. In the 2004 United States presidential election, George W. Bush carried the county by a massive 52.6% margin over John Kerry, making it Bush's strongest county in the slightly Democratic state, which Kerry won by a 2.5% margin over Bush. In 2008, John McCain carried Fulton by a 48.6% margin over Barack Obama, McCain's best showing in Pennsylvania, which Obama won by a 10.3% margin over McCain.[15] The county voted for Donald Trump in 2016 by a 70.8% margin, the highest in the state. The county has voted for the Republican in every presidential election since 1964. In 2006, Rick Santorum and Lynn Swann received more than 60% of the Fulton County vote despite their defeats statewide. In the 2012 election, Fulton County was the only county in Pennsylvania where Barack Obama won less than 25% of the white vote.[16]
Voter registration
[edit]As of February 5, 2024, there are 9,319 registered voters in the county. There are 6,851 registered Republicans, 1,523 registered Democrats, 674 voters registered non-affiliated voters, and 271 voters registered to other parties.[17]
Chart of Voter Registration
Law and government
[edit]Law enforcement
[edit]As of 2016[update] all areas in the county use the Pennsylvania State Police (PSP) in a law enforcement capacity, either with part-time police departments or with no other police departments.[18]
State Senate
[edit]- Judy Ward, Republican, Pennsylvania's 30th Senatorial District[19]
State House of Representatives
[edit]United States House of Representatives
[edit]United States Senate
[edit]Education
[edit]
There are three K-12 school districts:[20]
Transportation
[edit]Major highways
[edit] PA 16 - known as the Buchanan Trail, meets its western terminus in McConnellsburg; serves as a major two-lane through route across South-Central Pennsylvania, as it travels toward Waynesboro in Franklin County
PA 16 - known as the Buchanan Trail, meets its western terminus in McConnellsburg; serves as a major two-lane through route across South-Central Pennsylvania, as it travels toward Waynesboro in Franklin County PA 26 - this long Central Pennsylvania main street sees its final two miles run through the rural corner of Union Township, as it departs a long Bedford County stretch, before reaching the Maryland border
PA 26 - this long Central Pennsylvania main street sees its final two miles run through the rural corner of Union Township, as it departs a long Bedford County stretch, before reaching the Maryland border US 30 - a winding portion of the famous Lincoln Highway, the highway travels away from I-76, which parallels through most of the state's central mountains, to run across the county between the truck stop-lined Breezewood (East Providence Township) in Bedford County toward Franklin County's Chambersburg; although two-lane for its entire route, there is a limited access segment as the highway makes a short freeway bypass around McConnellsburg. the road serves as one of the county's two major arteries, largely oriented east/west, with its bypass intersecting US-522 just north of McConnellsburg.
US 30 - a winding portion of the famous Lincoln Highway, the highway travels away from I-76, which parallels through most of the state's central mountains, to run across the county between the truck stop-lined Breezewood (East Providence Township) in Bedford County toward Franklin County's Chambersburg; although two-lane for its entire route, there is a limited access segment as the highway makes a short freeway bypass around McConnellsburg. the road serves as one of the county's two major arteries, largely oriented east/west, with its bypass intersecting US-522 just north of McConnellsburg. I-70 - just prior to entering the county, the route breaks from its consignment with I-76, and it travels due south through a rural swath of the western portion of the county, as it connects with I-68 just across the Maryland line, along its way to Baltimore
I-70 - just prior to entering the county, the route breaks from its consignment with I-76, and it travels due south through a rural swath of the western portion of the county, as it connects with I-68 just across the Maryland line, along its way to Baltimore
 I-76 / Penna Turnpike - a portion of the Pennsylvania Turnpike, this toll interstate has one exit as it crosses the northern portion of the county; the Sideling Hill travel center is located Taylor Township
I-76 / Penna Turnpike - a portion of the Pennsylvania Turnpike, this toll interstate has one exit as it crosses the northern portion of the county; the Sideling Hill travel center is located Taylor Township PA 475 - a relatively short and highly rural range highway, it meets its southern terminus in Dublin Township, as it travels north through sparsely populated portions of Huntingdon County
PA 475 - a relatively short and highly rural range highway, it meets its southern terminus in Dublin Township, as it travels north through sparsely populated portions of Huntingdon County PA 484 - this short highway runs entirely within the county, serving the purpose of connecting I-70 with PA 26, as it runs across Union and Bethel Townships
PA 484 - this short highway runs entirely within the county, serving the purpose of connecting I-70 with PA 26, as it runs across Union and Bethel Townships US 522 - this route enters from Maryland to the south as part of a brief consignment with I-70, which it departs three miles into the county; the road serves as one of the county's two major arteries, largely oriented north–south, as it runs through McConnellsburg, past the county's only shopping center and through one of its only two stoplights, on its way to a junction with the Pennsylvania Turnpike in Dublin Township and toward Huntingdon County. it intersects with the US 30 bypass just north of McConnellsburg.
US 522 - this route enters from Maryland to the south as part of a brief consignment with I-70, which it departs three miles into the county; the road serves as one of the county's two major arteries, largely oriented north–south, as it runs through McConnellsburg, past the county's only shopping center and through one of its only two stoplights, on its way to a junction with the Pennsylvania Turnpike in Dublin Township and toward Huntingdon County. it intersects with the US 30 bypass just north of McConnellsburg. PA 643 - just seven miles in length, this very short access route connects I-70 with the hills of Bethel and Brush Creek Townships
PA 643 - just seven miles in length, this very short access route connects I-70 with the hills of Bethel and Brush Creek Townships PA 655 - this highway serves as a long, rural ridge route through the state's central mountains; its southern terminus is with the Maryland boundary in Thompson Township and it exits the county via Taylor Township toward Huntingdon County in the north
PA 655 - this highway serves as a long, rural ridge route through the state's central mountains; its southern terminus is with the Maryland boundary in Thompson Township and it exits the county via Taylor Township toward Huntingdon County in the north PA 731 - one of the shortest numbered routes in Pennsylvania, this five mile road connects I-70 with Route 484, as it runs entirely through Union Township
PA 731 - one of the shortest numbered routes in Pennsylvania, this five mile road connects I-70 with Route 484, as it runs entirely through Union Township PA 913 - a very rural access route through Bedford and Huntingdon Counties, this road's final miles are in Wells and Taylor Township
PA 913 - a very rural access route through Bedford and Huntingdon Counties, this road's final miles are in Wells and Taylor Township PA 915 - a mountain ridge cut-off-road, this highway travels from rural Bedford County along a valley setting toward its terminus with I-70 in Brush Creek Township
PA 915 - a mountain ridge cut-off-road, this highway travels from rural Bedford County along a valley setting toward its terminus with I-70 in Brush Creek Township PA 928 - a rural bi-state connector, this road travels from Ayr Township to the Maryland border via Thompson Township
PA 928 - a rural bi-state connector, this road travels from Ayr Township to the Maryland border via Thompson Township
Other
[edit]Fulton County is one of only two counties in Pennsylvania with no known active railroad lines of any kind, the other being Sullivan County.[21]
Communities
[edit]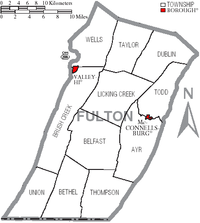
Under Pennsylvania law, there are four types of incorporated municipalities: cities, boroughs, townships, and, in at most two cases, towns. The following boroughs and townships are located in Fulton County:
Boroughs
[edit]- McConnellsburg (county seat)
- Valley-Hi
Townships
[edit]Unincorporated communities
[edit]Population ranking
[edit]The population ranking of the following table is based on the 2010 census of Fulton County.[22]
† county seat
| Rank | City/Town/etc. | Municipal type | Population (2010 Census) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Belfast | Township | 1,448 |
| 2 | † McConnellsburg | Borough | 1,220 |
| 3 | Needmore | CDP | 170 |
| 4 | Valley-Hi | Borough | 15 |
Census-designated places
[edit]See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Includes Westmoreland, Cambria, Fayette, Blair, Indiana, Somerset, Bedford, Huntingdon, Greene and Fulton Counties
- ^ "Census - Geography Profile: Fulton County, Pennsylvania". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved December 18, 2022.
- ^ "Find a County". National Association of Counties. Archived from the original on May 31, 2011. Retrieved June 7, 2011.
- ^ Fulton County, Pennsylvania Chamber of Commerce and Tourism Website Archived July 5, 2011, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Gannett, Henry (1905). The Origin of Certain Place Names in the United States. Govt. Print. Off. p. 133.
- ^ "2010 Census Gazetteer Files". United States Census Bureau. August 22, 2012. Retrieved March 7, 2015.
- ^ "PRISM Climate Group at Oregon State University".
- ^ "About the Appalachian Region". Appalachian Regional Commission. Retrieved June 20, 2024.
- ^ Woodard, Colin (July 30, 2018). "The Maps That Show That City vs. Country Is Not Our Political Fault Line". New York Times. Retrieved July 30, 2018.
- ^ "Geology, Map 13". www.dcnr.state.pa.us. Retrieved November 26, 2018.
- ^ "Geology, Map 59" (PDF). www.dcnr.state.pa.us. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved November 26, 2018.
- ^ "Geology, Map 11" (PDF). www.dcnr.state.pa.us. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved November 26, 2018.
- ^ "Census 2020".
- ^ "U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved January 31, 2008.
- ^ "P2 HISPANIC OR LATINO, AND NOT HISPANIC OR LATINO BY RACE – 2020: DEC Redistricting Data (PL 94-171) – Fulton County, Pennsylvania".
- ^ a b Leip, David. "Dave Leip's Atlas of U.S. Presidential Elections". uselectionatlas.org. Retrieved November 26, 2018.
- ^ Cohn, Nate (April 23, 2014). "Southern Whites' Loyalty to G.O.P. Nearing That of Blacks to Democrats (Map)". The New York Times. Retrieved April 27, 2014.
- ^ Pennsylvania Department of State (February 5, 2024). "Voter registration statistics by county". dos.pa.gov. Retrieved February 5, 2024.
- ^ Klibanoff, Eleanor (May 4, 2016). "Half of Pa. municipalities rely fully on state police". WHYY-TV. Retrieved July 23, 2024.
- ^ a b Center, Legislativate Data Processing. "Find Your Legislator". The official website for the Pennsylvania General Assembly. Retrieved May 11, 2017.
- ^ "2020 CENSUS - SCHOOL DISTRICT REFERENCE MAP: Fulton County, PA" (PDF). U.S. Census Bureau. Retrieved July 23, 2024. - Text list
- ^ "Penndot Railroad Map January 2015" (PDF). penndot.gov. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 9, 2022. Retrieved December 5, 2016.
- ^ "2010 U.S. Census website". United States Census Bureau. Retrieved February 10, 2013.